Are you hitting the gym, lifting heavy, and trying to build muscle, but feel like you're not getting the results you want? You've probably heard that protein is super important for muscle growth, and that's true! But knowing what to eat is just the start. There are many “secrets” and important details about protein for muscle gain that often get overlooked.
This article will dive deep into these hidden truths, helping you understand how to truly use protein to build the strong, muscular body you desire. We'll go beyond the basic advice and give you actionable tips that can make a real difference in your muscle-building journey. Get ready to unlock your full potential!
Key Takeaways
- More Than Just Quantity: It's not just about eating a lot of protein; the quality, timing, and distribution of your protein intake are just as vital for muscle growth.
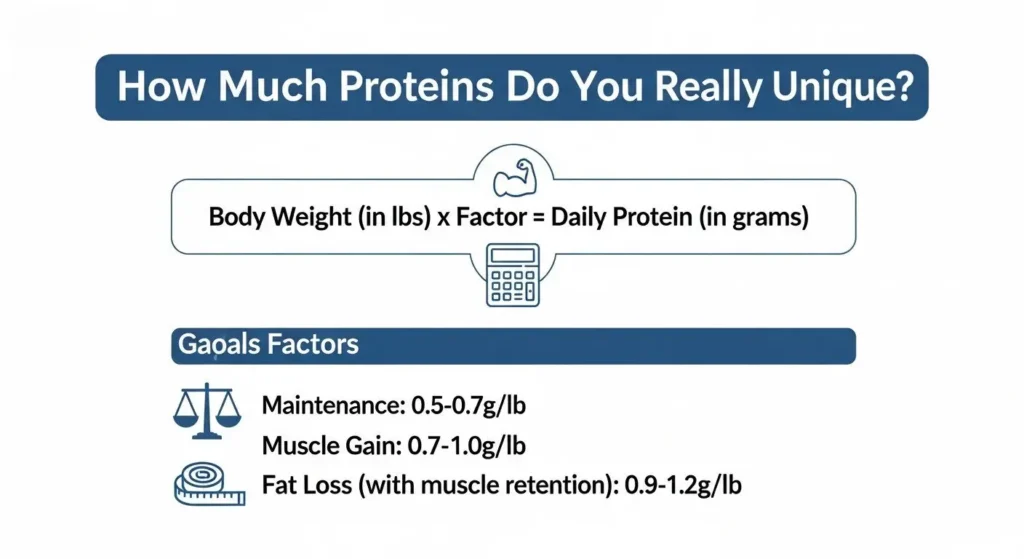
- Calculate Your Needs: Your ideal protein intake depends on your body weight, activity level, and goals. Use a calculator to find your personalized target, aiming for roughly 0.7-1.0 gram per pound of body weight.
- Diverse Protein Sources: Don't rely on just one type! Mix complete protein sources from both animal (meat, dairy, eggs) and plant-based foods (legumes, tofu) to get all essential amino acids.
- Fuel Beyond Protein: Remember that carbohydrates provide energy for intense workouts, and healthy fats are crucial for hormones. Sleep, hydration, and consistent training are also non-negotiable for muscle building.
- Avoid Common Mistakes: Don't fall into traps like under-eating, over-relying on supplements, or ignoring overall diet quality. A balanced, consistent approach is key to long-term success.
The Basics of Protein for Muscle Gain: Your Body's Building Blocks
Let's start with the basics. You know protein is important, but do you know why? Think of your body as a magnificent house. Protein isn't just the bricks; it's also the mortar, the wood, and even the repair crew!
Protein is a macronutrient, just like carbohydrates and fats. But its role is unique. It's made up of smaller units called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids, and your body can make some of them. However, nine of them are “essential,” meaning you must get them from your food. These essential amino acids are the true stars when it comes to building and repairing muscle.
How Does Protein Build Muscle?
When you work out, especially with weights, you create tiny tears in your muscle fibers. This might sound bad, but it's actually the first step in muscle growth! Your body then uses protein for muscle gain to repair these tears. But it doesn't just repair them; it makes them stronger and a little bigger than before. This process is called muscle protein synthesis (MPS).
- Repair: Protein helps fix the damage done during exercise.
- Growth: It provides the raw materials to build new muscle tissue.
- Strength: Over time, this leads to stronger, larger muscles.
Without enough protein, your body can't effectively repair and rebuild. It's like trying to build that house without enough bricks – it just won't happen efficiently, if at all.
The “Anabolic Window”: Myth or Reality?
You might have heard that you must eat protein within 30-60 minutes after your workout, or you'll miss your “anabolic window” and all your hard work will be wasted! 😱 While it's a good idea to eat a balanced meal with protein after a workout, the strict “anabolic window” idea isn't as critical as once thought.
Here's the secret: Your muscles stay sensitive to protein for many hours after exercise, even up to 24-48 hours! So, while getting protein for muscle gain soon after your workout is beneficial, don't stress if you can't eat immediately. What's far more important is your total daily protein intake and how you distribute it throughout the day. We'll talk more about this soon!
How Much Protein Do You Really Need? (Beyond the General Advice)
This is one of the biggest “secrets” because everyone's needs are different! The general advice you see on food labels (like 50 grams per day) is for average, inactive people. If you're serious about building muscle, you'll need significantly more.
Calculating Your Personalized Protein Needs
To figure out your specific needs, we need to consider a few things:
- Your Body Weight: This is the main factor.
- Your Activity Level: How often and intensely do you work out?
- Your Goals: Are you trying to build muscle (bulk), maintain muscle while losing fat (cut), or just maintain?
A good starting point for most people looking to gain muscle is 0.7 to 1.0 gram of protein per pound of body weight (or 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight).
Let's do some quick math:
- Example 1: A person weighing 150 lbs (about 68 kg) aiming for muscle gain.
- 150 lbs * 0.8 grams/lb = 120 grams of protein per day
- 150 lbs * 1.0 gram/lb = 150 grams of protein per day
- So, this person should aim for 120-150 grams of protein daily.
- Example 2: A person weighing 200 lbs (about 91 kg) aiming for muscle gain.
- 200 lbs * 0.8 grams/lb = 160 grams of protein per day
- 200 lbs * 1.0 gram/lb = 200 grams of protein per day
- This person should aim for 160-200 grams of protein daily.
You might notice that the higher end (1.0 g/lb) is often recommended for those who are very active, lifting heavy, or in a calorie deficit (trying to lose fat while keeping muscle). When you're cutting calories, higher protein helps prevent muscle loss.
💡 Pull Quote: “Don't just guess your protein intake. Calculate it! Your body needs a specific amount to thrive and build muscle, and that amount is unique to you.”
Consistency is King
It's not enough to hit your protein target one day and then forget about it the next. Muscle building is a continuous process. Your body needs a steady supply of amino acids day in and day out to keep repairing and growing. Make it a habit to track your protein for muscle gain for a while until you get a good feel for what your daily meals provide.
The Best Sources of Protein (Quality Over Quantity)
Not all protein is created equal! Some sources are better than others because they provide all the essential amino acids your body needs. These are called complete proteins.
Complete Protein For Muscle Gains: The Muscle Builders
Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids. Most anmal-based proteins fall into this category.
Top Animal Protein Sources:
- Lean Meats: Chicken breast, turkey, lean beef, pork loin. (Excellent for a high protein punch with less fat.)
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, cod, tilapia. (Often rich in healthy omega-3 fatty acids too!)
- Eggs: The “perfect protein” – affordable and versatile. (One large egg has about 6 grams of protein.)
- Dairy Products: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, milk, whey protein. (Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are packed with protein and often contain casein, a slow-digesting protein.)
Plant-Based Powerhouses: Combining for Completeness
Many plant-based foods are considered “incomplete” proteins because they might be low in one or more essential amino acids. However, by eating a variety of plant proteins throughout the day, you can easily get all the essential amino acids your body needs for protein for muscle gain. This is called protein combining.
Excellent Plant Protein Sources:
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, kidney beans. (Great in soups, salads, or as a side.)
- Tofu & Tempeh: Soy-based products that are very versatile and absorb flavors well. (Often considered complete proteins themselves!)
- Quinoa: A grain that is also a complete protein. (Use it instead of rice for an extra protein boost.)
- Nuts & Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flax seeds, pumpkin seeds. (Good for snacks or adding to meals, but be mindful of calories.)
- Seitan: A wheat-based protein with a meaty texture.
- Edamame: Young soybeans, great as a snack or in stir-fries.
Protein Supplements: When Do You Need Them?
Protein powders (like whey, casein, or plant-based blends) are supplements, meaning they are meant to supplement your diet, not replace whole foods.
When supplements can be helpful:
- Convenience: Quick and easy way to get protein when you're busy or on the go.
- Hitting Targets: If you struggle to eat enough whole food protein to meet your daily goal.
- Post-Workout: Whey protein is fast-digesting, making it a good option after a workout for quick amino acid delivery.
- Dietary Restrictions: Plant-based protein powders are excellent for vegans or those with dairy allergies.
The secret: Don't rely too heavily on supplements. Whole foods offer a wider range of nutrients, fiber, and micronutrients that supplements often lack. Aim to get most of your protein from food, and use supplements to fill in the gaps.

Timing is Everything (But Not How You Think)
We already debunked the super-strict “anabolic window.” The real secret to protein timing for muscle gain is spreading your protein for muscle gain intake throughout the day.
Distribute Your Protein Evenly
Instead of eating one huge protein meal, aim for 3-5 servings of protein for muscle gain throughout the day, with each serving containing 20-40 grams of protein. This steady supply keeps your muscles in an “anabolic” (building) state for longer.
Think of it like this: your body can only use so much protein at once for muscle building. Flooding it with 80 grams in one meal might mean some of that protein gets used for energy or other functions, rather than muscle repair. Smaller, more frequent protein for muscle gains are more efficient.
Example Daily Protein for Muscle Gain Distribution (for a 150lb person aiming for 120-150g):
- Breakfast: 30g (e.g., eggs, Greek yogurt)
- Lunch: 35g (e.g., chicken salad)
- Snack: 20g (e.g., cottage cheese or protein shake)
- Dinner: 40g (e.g., salmon with veggies)
- Pre-bed: 20g (e.g., casein shake or cottage cheese)
- Total: 145g
Pre- and Post-Workout Protein for Muscle Gain: Still Important
While the “window” isn't as narrow as once thought, having protein for muscle gain around your workout is still beneficial.
- Pre-Workout: A small amount of protein (e.g., 20-25g) before your workout can help reduce muscle breakdown during exercise and get amino acids ready for repair. Combine it with some carbs for energy!
- Post-Workout: A protein-rich meal or shake after your workout helps kickstart the recovery and muscle repair process. Focus on complete protein for muscle gain.
Casein Before Bed: Your Nighttime Muscle Repair Crew
Casein protein is a slow-digesting protein found in dairy. Because it releases amino acids slowly over several hours, it's an excellent choice to have before bed. This provides a steady stream of building blocks to your muscles while you sleep, preventing muscle breakdown during your fasting period. Cottage cheese is a great whole-food source of casein!
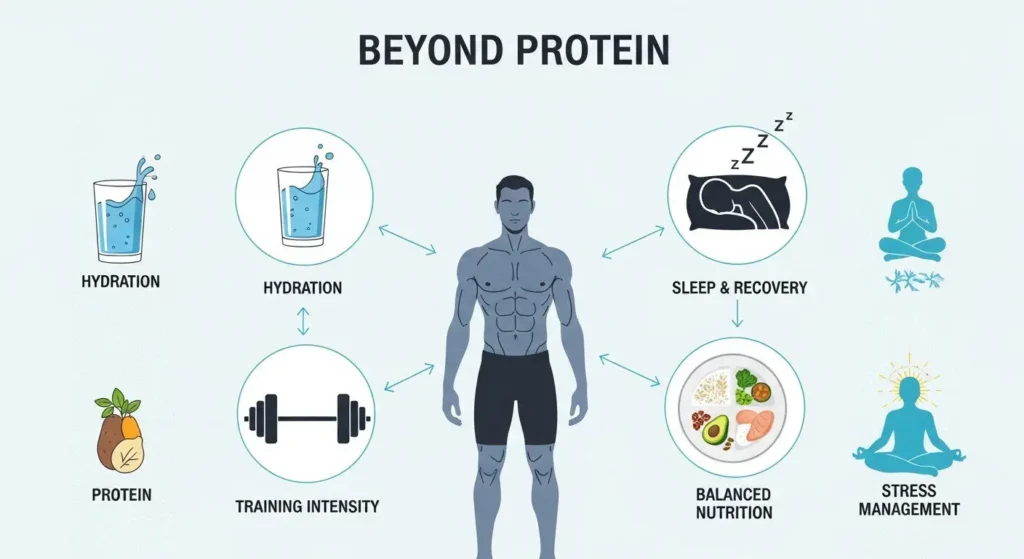
Beyond Protein: Synergistic Factors for Muscle Gain
Protein is a crucial piece of the puzzle, but it's not the only piece. Many other factors work together with protein to help you build muscle effectively. Ignoring these is a major “secret” that holds many people back!
Carbohydrates and Fats: Your Energy and Hormone Helpers
- Carbohydrates: These are your body's primary energy source. Without enough carbs, your body might start using protein for energy instead of muscle building. Carbs also help replenish glycogen stores in your muscles, which are vital for intense workouts. Think whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and potatoes.
- Healthy Fats: Essential for hormone production (including testosterone, which is important for muscle growth), nutrient absorption, and overall health. Don't skip them! Sources include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish.
Hydration: The Unsung Hero
Your muscles are about 75% water! Even slight dehydration can lead to decreased performance, fatigue, and impaired recovery. Make sure you're drinking plenty of water throughout the day, especially around your workouts. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses (2-3 liters) daily.
Sleep and Recovery: When Muscles Really Grow
You don't grow in the gym; you grow outside the gym, especially when you sleep! During deep sleep, your body releases growth hormone, which is vital for muscle repair and growth. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep every night. Prioritizing rest and recovery is just as important as your training and nutrition.
Training Intensity and Progressive Overload: The Stimulus
You can eat all the protein in the world, but if you're not challenging your muscles, they won't grow. Progressive overload means gradually increasing the demands on your muscles over time. This could be:
- Lifting heavier weights.
- Doing more repetitions.
- Increasing sets.
- Reducing rest times.
- Improving your form.
Without this stimulus, your muscles have no reason to adapt and grow stronger.
Stress Management: The Silent Muscle Killer
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, a hormone that can break down muscle tissue and hinder recovery. Finding ways to manage stress, whether through meditation, hobbies, or spending time in nature, is crucial for your overall health and muscle-building success.
Overall Health: A Foundation for Growth
Your body works as a whole system. If other areas of your health are struggling, your ability to build muscle will be impacted. For men, maintaining good prostate health is vital for overall well-being, which in turn supports physical performance and recovery. Learning about the most effective prostate supplements reviewed for 2025 or understanding how ProstaVive: Tackling Prostate Problems Head-On can contribute to your long-term health, which indirectly supports your fitness goals. A comprehensive guide to prostate supplements: understanding and your choice can help you make informed decisions. Remember, products like ProstaVive: The Natural Solution for Prostate Health are designed to support this critical area of male health.
Similarly, liver health plays a key role in metabolism and nutrient processing, including proteins. If you're interested in how liver health impacts your overall well-being and weight management, checking out Liv Pure reviews could offer valuable insights. A healthy body is a body that can build muscle efficiently.
Common Protein Mistakes to Avoid
Even with good intentions, many people make mistakes that hinder their muscle-building progress. Here are some “secrets” about what not to do:
1. Not Eating Enough Protein (The Most Common Mistake!)
This goes back to calculating your needs. Many people underestimate how much protein they actually need, especially if they're very active. If you're consistently falling short of your daily target, your muscles won't have the building blocks they need to grow.
2. Eating Too Much Protein at Once
While your body can process a good amount of protein, there's a limit to how much it can use for muscle protein synthesis in a single sitting. As discussed, spreading your intake is more effective than trying to cram it all into one or two massive meals. Aim for 20-40 grams per meal/snack.
3. Relying Solely on Supplements
Protein shakes are convenient, but they shouldn't be your main source of protein. Whole foods provide a wider array of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and other beneficial compounds that are essential for overall health and optimal muscle growth. Think of supplements as a “boost,” not a replacement.
4. Ignoring Overall Diet Quality
It's not just about protein. If your diet is full of processed foods, unhealthy fats, and refined sugars, even high protein intake won't be as effective. Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods. This means plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean protein sources.
5. Not Adjusting Protein for Different Phases
Your protein needs might change depending on your goal.
- Bulking (Gaining Muscle): You might need slightly less protein per pound of body weight, as you'll have plenty of calories from carbs and fats to spare protein for muscle building.
- Cutting (Losing Fat): You might need more protein per pound of body weight. When you're in a calorie deficit, higher protein helps preserve your hard-earned muscle mass while you lose fat.
6. Forgetting About Digestive Health
Even if you eat enough protein, if your digestive system isn't working well, you might not be absorbing all those valuable amino acids. Eating fermented foods, getting enough fiber, and staying hydrated can support a healthy gut. If you have persistent digestive issues, consider talking to a doctor or dietitian.

Special Considerations for Protein and Muscle Gain
Muscle building isn't a one-size-fits-all journey. Here are some extra “secrets” that might apply to you:
Age-Related Muscle Loss (Sarcopenia)
As we get older, our bodies naturally start to lose muscle mass and strength, a condition called sarcopenia. To combat this, older adults actually need more protein per pound of body weight than younger adults to maintain and build muscle. They also benefit greatly from resistance training. So, if you're over 50, don't shy away from that protein!
Vegetarian and Vegan Protein Strategies
It's absolutely possible to build significant muscle on a plant-based diet! The key is variety and smart combining.
- Combine Proteins: Pair legumes with grains (e.g., beans and rice), nuts with seeds, or use complete plant proteins like quinoa, tofu, tempeh, and seitan.
- Increase Overall Intake: Plant proteins can be less dense in protein per serving compared to animal proteins, so you might need to eat slightly larger portions or more frequent meals to hit your targets.
- Supplement Wisely: Plant-based protein powders (pea, rice, soy, hemp blends) can be very helpful for meeting your needs.
Listening to Your Body
Ultimately, your body will give you clues. Are you recovering well? Are you feeling energized? Are you seeing progress in the gym? If not, review your protein intake, your overall diet, your training, and your recovery. Sometimes, small adjustments can lead to big breakthroughs.
Conclusion: The Real Secrets to Protein for Muscle Gain
The “secrets” to using protein for muscle gain aren't really secrets at all—they're often overlooked fundamentals! It's about moving beyond the basic advice and understanding the nuances:
- Know Your Number: Calculate your personal protein needs based on your body and goals.
- Quality Matters: Choose a variety of complete protein sources from both animal and plant foods.
- Spread It Out: Distribute your protein intake evenly throughout the day for maximum muscle protein synthesis.
- Holistic Approach: Remember that protein works best when supported by adequate carbs and fats, proper hydration, quality sleep, consistent training, and overall good health.
- Avoid Pitfalls: Be mindful of common mistakes like under-eating or over-relying on supplements.
Building muscle is a marathon, not a sprint. It requires consistency, patience, and a smart approach to nutrition. By applying these “secrets,” you'll be well on your way to building the strong, healthy physique you've been working for. Keep learning, keep lifting, and keep fueling your body right.







